Downloads

Download working paper here
PDF | 847.81 KB
One-quarter of married, fertile-age women in Sub-Saharan Africa report not wanting a pregnancy and yet do not practice contraception. We collect detailed data on the subjective beliefs of married, adult women not wanting a pregnancy and estimate a structural model of contraceptive choices. Both our structural model and a validation exercise using an exogenous shock to beliefs show that correcting women’s beliefs about pregnancy risk absent contraception can increase use considerably. Our structural estimates further indicate that costly interventions like eliminating supply constraints would only modestly increase contraceptive use, while confirming the importance of partners’ preferences highlighted in related literature.
Authors

Grant Miller

Research Fellow University College London
Áureo is an applied econometrician with strong interests in both methodological and empirical questions, affiliated with UCL, Cemmap, IFS and CEPR.

Christine Valente
Working Paper details
- DOI
- 10.1920/wp.ifs.2025.1625
- Publisher
- Institute for Fiscal Studies
Suggested citation
G, Miller and C, Valente and Á, de Paula. (2025). Subjective expectations and demand for contraception. 25/16. London: Institute for Fiscal Studies. Available at: https://ifs.org.uk/publications/subjective-expectations-and-demand-contraception-1 (accessed: 12 April 2025).
More from IFS
Understand this issue
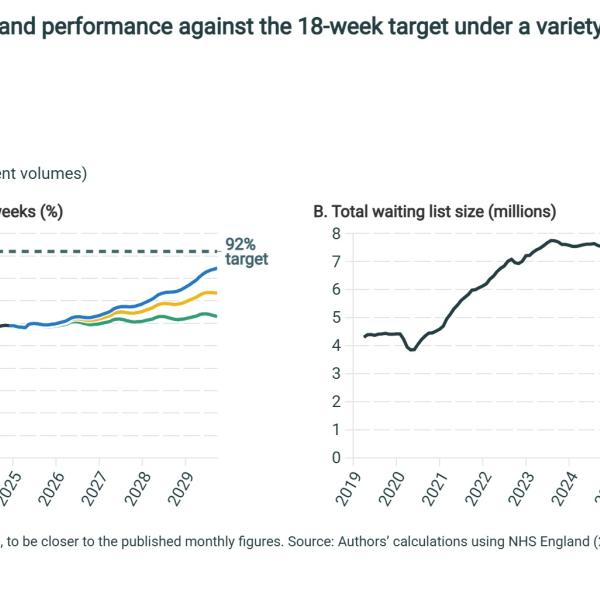
Simulated list size and performance against the 18-week target under a variety of treatment growth rate assumptions
Although performance improves in each case, in none of our scenarios does performance reach the 92% target by the end of the parliament.
20 March 2025
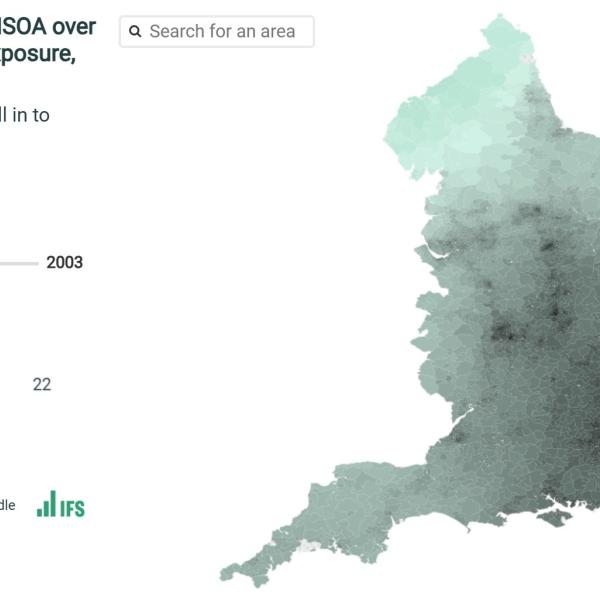
Air pollution in England by MSOA over time, measured by PM2.5 exposure, 2003 to 2023
Average exposure to PM2.5 in England fell by 54% between 2003 and 2023. Almost everywhere in England is now below England’s 2040 target for PM2.5.
6 December 2024
Can the new government fix the NHS?
14 August 2024
Policy analysis

Enlisting consumers in tax enforcement: a policy review
This paper examines the rise of consumer incentives in tax enforcement and the conditions under which they can enhance compliance and raise revenue.
31 March 2025

Can the government achieve its 18-week elective waiting time target?
Simulation modelling of NHS elective waiting times in England shows that the government’s 18-week target is unlikely to be met in this parliament.
20 March 2025
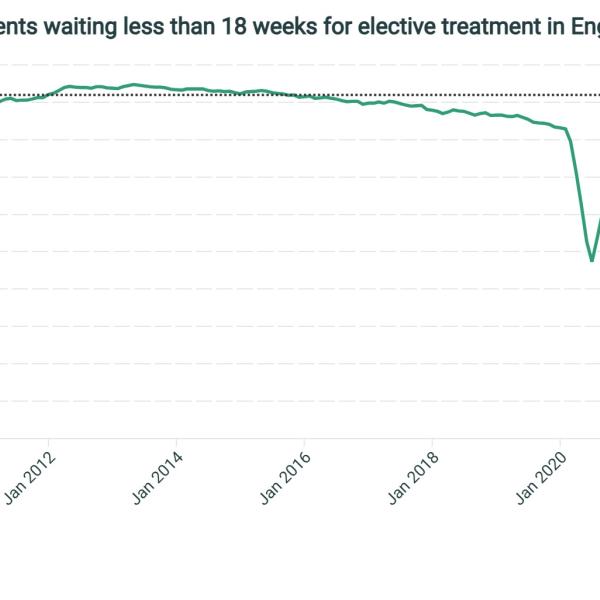
Percentage of patients waiting less than 18 weeks for elective treatment in England
Performance against the NHS' 18-week waiting times target has since deteriorated gradually before a sharp fall during the pandemic.
20 March 2025
Academic research
Call for papers: IFS-ADBI-GHE Workshop on Health Economics in LMICs 2025
Submissions are open until 15th February for the IFS-GHE Workshop on Health Economics in LMIC 2025

The menopause "penalty"
We show that a menopause diagnosis leads to lasting drops in earnings and employment, alongside greater reliance on social transfers.
21 March 2025

TaxDev collaborating with Government of Ghana on VAT, customs, and distributional analysis
Ghana Ministry of Finance officials explain how the partnership with TaxDev is helping to improve tax policy analysis
24 February 2025