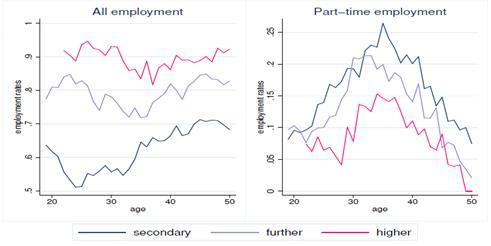
We estimate a dynamic model of employment, human capital accumulation—including education, and savings for women in the United Kingdom, exploiting tax and benefit reforms, and use it to analyze the effects of welfare policy. We find substantial elasticities for labor supply and particularly for lone mothers. Returns to experience, which are important in determining the longer-term effects of policy, increase with education, but experience mainly accumulates when in full-time employment. Tax credits are welfare improving in the U.K., increase lone-mother labor supply and marginally reduce educational attainment, but the employment effects do not extend beyond the period of eligibility. Marginal increases in tax credits improve welfare more than equally costly increases in income support or tax cuts.
Figure. Female employment over the course of life
Authors

CPP Co-Director
Richard is Co-Director of the Centre for the Microeconomic Analysis of Public Policy (CPP) and Senior Research Fellow at IFS.

Research Fellow Yale University
Costas is a Research Fellow of the IFS and a Professor of Economics at Yale University and a Visiting Professor at University College London.

Research Fellow Financial Conduct Authority
Jonathan is a Research Fellow at the IFS and a Technical Specialist in the Economics Department at the Financial Conduct Authority.

Deputy Research Director
Monica is a Deputy Research Director and Professor of Economics at the University of Bristol, with an interest in Labour, Family and Public Economics.
Journal article details
- DOI
- 10.3982/ECTA11576
- Publisher
- The Econometric Society
- Issue
- Volume 84, Issue 5, September 2016
Suggested citation
Blundell, R et al. (2016). 'Female labor supply, human capital, and welfare reform' 84(5/2016)
More from IFS
Understand this issue
If you can’t see it, you can’t be it: role models influence female junior doctors’ choice of medical specialty
24 April 2024

Sure Start achieved its aims, then we threw it away
15 April 2024

A mess has been made of Child Benefit, and the clear-up operation may not be easy
29 March 2024
Policy analysis

Recent trends in and the outlook for health-related benefits
19 April 2024

4.2 million working-age people now claiming health-related benefits, could rise by 30% by the end of the decade
19 April 2024

Gap between higher- and lower-paid public sector workers falls by more than a third since 2007 as doctors and experienced teachers have faced unprecedented pay cuts
26 March 2024
Academic research

Labour market inequality and the changing life cycle profile of male and female wages
15 April 2024

There and back again: women’s marginal commuting costs
2 April 2024

Imagine your life at 25: Gender conformity and later-life outcomes
24 April 2024