As in many European countries, labour productivity in the UK has been stagnant since the start of the Great Recession. This article uses individual data on employment and wages to try to understand whether real wage flexibility can help shed light on the UK’s productivity puzzle. It finds, perhaps unsurprisingly, that workforce composition cannot explain the reduction in wages and hence productivity that we observe, even compared to previous recessions; instead, real wages have fallen significantly within jobs this time round. Why? One possibility we investigate is that the labour supply in the UK is higher compared to previous recessions.
Find the working paper here.
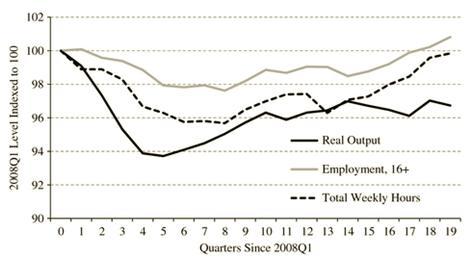
Figure. Changes to UK output, employment and hours
Authors

CPP Co-Director
Richard is Co-Director of the Centre for the Microeconomic Analysis of Public Policy (CPP) and Senior Research Fellow at IFS.

Research Fellow University College London
Claire is a Research Fellow at IFS, working on the determinants and consequences of participation in childcare and education for parents and children.

Research Associate
Wenchao is an Assistant Professor at the University of Sussex and an IFS Research Associate.
Journal article details
- DOI
- 10.1111/ecoj.12138
- Publisher
- Wiley
- Issue
- May 2014
Suggested citation
R, Blundell and C, Crawford and W, Jin. (2014). 'What can wages and employment tell us about the UK's productivity puzzle?' (2014)
More from IFS
Understand this issue
If you can’t see it, you can’t be it: role models influence female junior doctors’ choice of medical specialty
24 April 2024

Sure Start achieved its aims, then we threw it away
15 April 2024
The NHS waiting list: when will it come down?
29 February 2024
Policy analysis

The short- and medium-term impacts of Sure Start on educational outcomes
9 April 2024

Sure Start greatly improved disadvantaged children’s GCSE results
9 April 2024
Progression of nurses within the NHS
12 April 2024
Academic research

Labour market inequality and the changing life cycle profile of male and female wages
15 April 2024

Interpreting cohort profiles of lifecycle earnings volatility
15 April 2024

There and back again: women’s marginal commuting costs
2 April 2024